Pineal gland
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Pineal gland | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Endocrine system | |
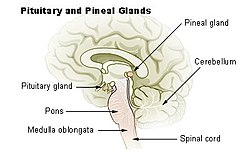 | |
| Diagram of pituitary and pineal glands. | |
| Latin | glandula pinealis |
| Gray's | subject #276 1277 |
| Artery | superior cerebellar artery |
| Precursor | Neural Ectoderm, Roof of Diencephalon |
| MeSH | Pineal+gland |
The pineal gland (also called the pineal body, epiphysis cerebri, epiphysis or the "third eye") is a small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain. It produces melatonin, a hormone that affects the modulation of wake/sleep patterns and photoperiodic (seasonal) functions.[1][2] It is shaped like a tiny pine cone (hence its name), and is located near to the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two rounded thalamic bodies join.
No comments:
Post a Comment