It is often the forces, or bonds, between the atoms which provide the initial clues about why certain substances have specific properties
The nature of the bond dictates many of the physical properties of a substance - viz. the remarkable differences between diamond and graphite, though they are both forms
of Carbon.
What holds electrically neutral atoms together into molecules and even larger groups - as liquids and solids ?
Bonding between atoms to form large aggregates is possible when the energy of the combined system is less than that of the system of separate noninteracting atoms.
Stability of bonding is determined by
(i) Coulomb attraction between opposite charges (Potential Energy contribution) and
(ii) lowering of Kinetic Energy by delocalization of the wavefunction of the electrons participating in the bonding.
We will look at four types of bonds: covalent, ionic, metallic and Van der Waals [Hydrogen bond is essentially an especially strong type of Van der Waals bond].
Bonds between atoms are of the followng types:
Ionic bonds
Covalent bonds
Metallic bonds
What are the possibilities when two atoms are brought close to each other ?:
1. A covalent bond is formed - through sharing of one or more pairs of electrons by the two atoms - the KE of participating electrons is lowered (by Uncertainty Principle)
2. An ionic bond is formed - an extreme case of covalent bond, when one or more electrons from one atom is transferred to the other
3. No bond is formed - when the electronic structure of two atoms overlap they form a single system and are subject to Pauli exclusion principle - may result in electrons being pushed to higher energy states making the bond unstable. .
Mechanism of the Covalent Bond
How is it possible for two nuclei to share an electron -- quantum tunneling of the electron wavefunction with high frequency
Why electron sharing leads to lower total energy and a stable system -- if the electron occupies a larger volume, the uncertainty principle implies lower momentum and hence lower KE.
.
Examples:
- H2+ molecular ion (2 protons, 1 electron): spatially symmetric wavefunction most stable giving a bond energy of 2.65 eV.
- H2 molecular ion (2 protons, 2 electrons): spatially symmetric, spin antiparallel wavefunction most stable.
- Complex molecules: the stability of the bonding is determined by the outermost (valence) electrons only. Alterations in the valence electron wavefunctions due to interaction with other atoms determine the geometry of the bond and gives rise to the directed nature of covalent molecular bonds. Example: tetrahedral structure of diamond, methane (CH4).
Bottomline:
All covalent crystals are hard (diamond is the hardest substance known), have high melting point, are insulators and are insoluble in all ordinary liquids. Cohesive energies of 6-12 eV/atom are typical for covalent bonds.
Looking further ?
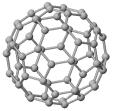 | Fullerenes (e.g., C60, pictured on the left ) are formed by sp2 type of covalent bonds between neighboring Carbon atoms. |
agen taruhan sabung ayam terpercaya
ReplyDeleteMau bonus ? klik disini ya ayam jago bangkok
ReplyDeleteVidio Ayam Sabung
ReplyDeleteBANDAR JUDI SLOT PALING LENGKAP DENGAN 1 USERID BISA MEMAINKAN SEMUA PERMAINAN
ReplyDeleteWELCOME BONUS UNTUK PERMAINAN SLOT 50% MAKSIMAL 1.000.000 IDR
WELCOME BONUS UNTUK SEMUA JENIS PERMAINAN 20%
TO DI JAMIN RENDAH !!!
DEPOSIT BANK LOCAL :
BCA - MANDIRI - BNI - BRI - DANAMON - JENIUS BTPN DLL
DEPOSIT E-CASH :
OVO - DANA - LINKAJA - GOPAY - SAKUKU
DEPOSIT PULSA (DEPOSIT NON RATE/ALIAS TANPA POTONGAN) :
-> TELKOMSEL
-> XL / AXIS
Demo SLOT
Slot Joker Jewel
LINK AKSES :
Agen Togel
Situs Togel Online
Museumbola Slot Habanero
Museumbola Slot Pragmatic